A bunion is a painful, bony lump that develops at the joint where the big toe meets the foot. It forms when the big toe gradually shifts towards the other toes, causing the joint to protrude 拇趾外翻治療. Bunions can cause discomfort, swelling, and difficulty walking. They often worsen over time if not treated properly.
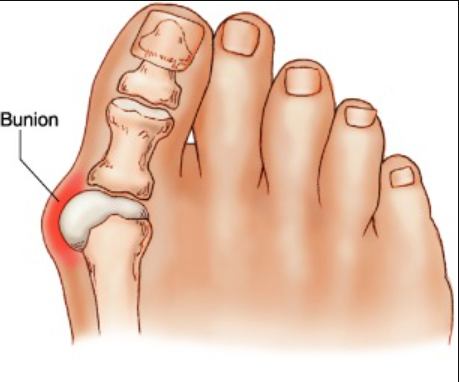
What Causes a Bunion?
Bunions develop due to pressure and misalignment of the bones in the foot. Several factors contribute to their formation:
- Genetics – A family history of bunions increases the likelihood of developing them.
- Improper Footwear – Tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes force the toes into an unnatural position, leading to bunions.
- Flat Feet or High Arches – Foot structure abnormalities can increase the risk of bunions.
- Arthritis – Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can weaken the joints and contribute to bunion formation.
- Injury or Stress on the Feet – Repetitive stress from standing for long hours or engaging in high-impact activities can worsen bunions.
Common Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions develop gradually and can cause various symptoms, including:
- A visible bump on the side of the big toe joint
- Swelling, redness, and tenderness around the affected area
- Persistent foot pain, especially while walking or wearing tight shoes
- Difficulty moving the big toe
- Corns or calluses due to friction between toes
How to Prevent Bunions
While some people are genetically predisposed to bunions, taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk:
✔ Wear Comfortable Shoes – Choose footwear with a wide toe box and proper arch support.
✔ Avoid High Heels – Limit wearing high heels or narrow shoes that put pressure on the toes.
✔ Use Orthotic Insoles – These can help distribute weight evenly and prevent foot misalignment.
✔ Practice Foot Exercises – Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve toe mobility and prevent stiffness.
✔ Maintain a Healthy Weight – Excess weight puts additional pressure on the feet and can contribute to bunion formation.
Treatment Options for Bunions
Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild to moderate bunions, non-surgical approaches can help relieve pain and slow progression:
- Wearing Proper Footwear – Switching to shoes with more room for the toes can ease discomfort.
- Bunion Pads and Toe Spacers – These help reduce pressure and prevent friction.
- Ice Therapy – Applying ice packs can reduce swelling and pain.
- Pain Relievers – Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Physical Therapy – Foot exercises improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting the toe joint.
Surgical Treatment
If a bunion becomes severe and affects daily activities, surgery may be necessary. Bunionectomy is a common procedure where the bone is realigned to correct the deformity. Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the bunion and the type of surgery performed.
Conclusion
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause pain and discomfort if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies can help minimize the risk. If you experience persistent pain or difficulty walking due to a bunion, consult a doctor for appropriate treatment. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve foot health.